rendering
Rendering Tools and Utilities
Jump to
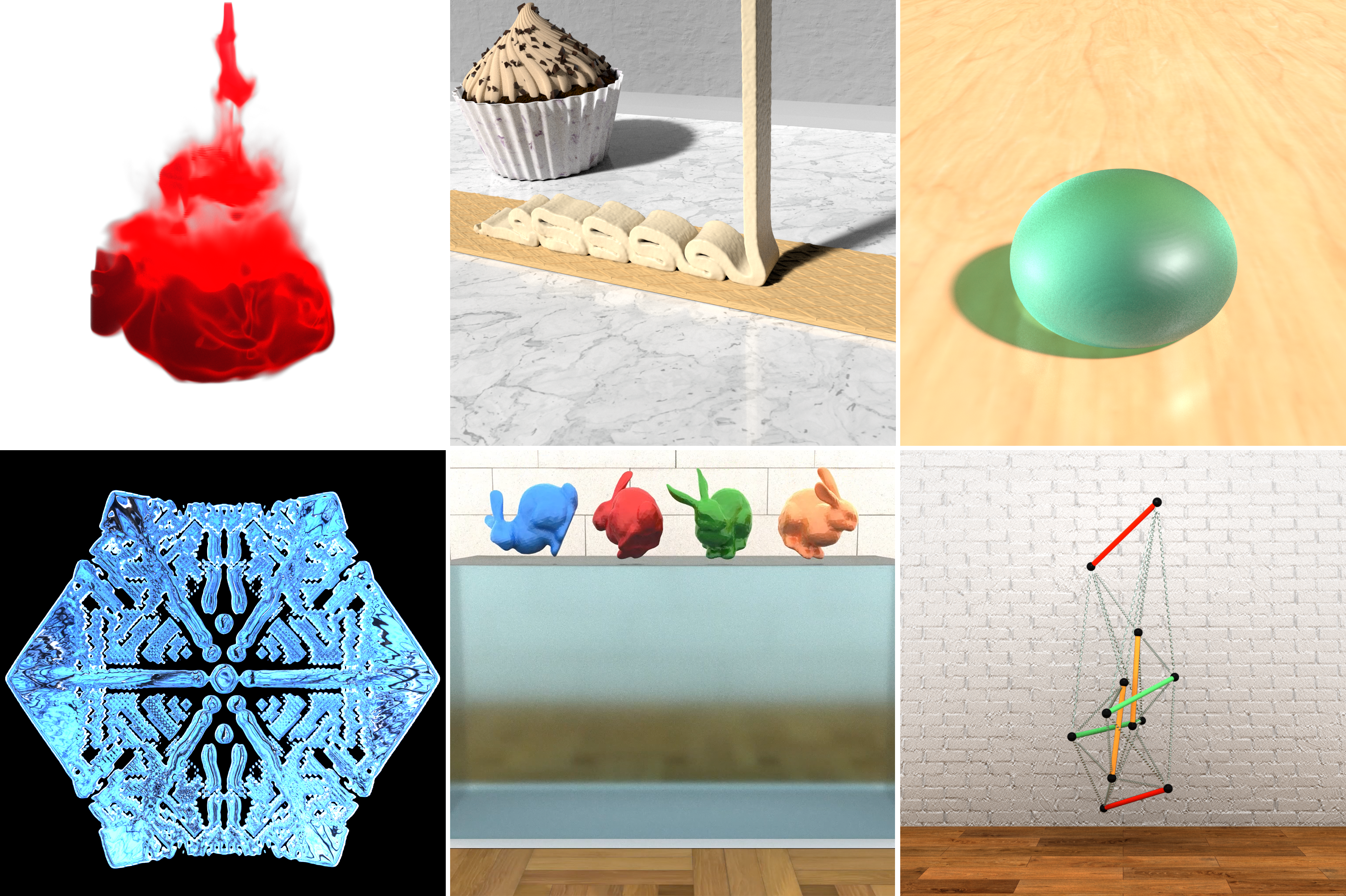 Figure: A collection of renderings from the publications.
Figure: A collection of renderings from the publications.
Preface
This is a growing collection of tools used to generate offline renderings and animation for research in Computer Graphics at Laboratory for Interactive Virtual Environments (LIVE). LIVE is directed by Mridul Aanjaneya at Department of Computer Science, Rutgers University. This collection is created and maintained by Chengguizi Han from LIVE. Any questions and suggestions are welcome.
Huge thanks to all other contributors to the publications:
- The members (and alumni) of LIVE: Dr. Tao Xue, Haozhe Su.
- Prof. Chenfanfu Jiang at UCLA Mathematics.
- Kun Wang and Prof. Kostas Bekris at Rutgers Robotics PRACSYS Group.
Contents
- Get Started: introduction to softwares, tools, and general rendering process
- Bash Commands: commonly used bash commands
- Bash Scripts: commonly used bash scripts that takes inputs
- Python Scripts: with python from shell
- render.py: batch render RIB files
- convert.py: convert particles positions in TXT to OBJ/RIB
- Content Creation Softwares: download pages and recommended tutorials
- Q&A: common questions
- Resources: other useful resources
- Publications: more examples using this rendering process
Get Started
- Softwares or tools recommended:
- Maya or Blender
- for 3D content creation: modeling, animation
- use with renderer plugin
- RenderMan and RenderMan for Maya
- standalone renderer and its plugin: shading, lighting
- can render with RIB (RenderMan Interface Bytestream) file with command
prman -progress <file-name>.rib
- Python
- Python for Maya (cheat-sheet): batch modification in Maya
- batch rendering with RIB files
- Houdini
- convert particles to mesh
- Mitsuba renderer 0.6 utilities
- convert EXR to PNG with
mtsutil tonemap -t *.exr
- convert EXR to PNG with
- Maya or Blender
- General Process Description
- Simulation: prepare data
- Planning
- Features: know the strength and purpose of the data, that determines the way of representation:
- close-up look or zoomed-out view
- particles or meshed objects
- simple or detailed scene
- Environment: find a rational and interesting scene with the data
- Features: know the strength and purpose of the data, that determines the way of representation:
- Set up the environment in 3D softwares
- Modeling
- low-poly modeling
- meshing from particles, with Houdini
- find free 3D models at turbosquid, sketchfab
- find and follow tutorial for 3D modeling
- UV Editing (optional)
- Shading (Textures, Materials)
- use renderer’s shading node (e.g PxrSurface with RenderMan)
- find free textures at textures.com
- Lighting
- use renderer’s lighting node (e.g PxrDomeLight with RenderMan)
- Camera
- set aspect ratio, usually 1240x1024
- Animation
- with built-in tools
- with data, using Python (for Maya)
- Modeling
- Rendering
- with built-in renderer (e.g Arnold in Maya, Cycles in Blender)
- with plug-in renderer (e.g RenderMan in Maya or Blender)
- with standalone renderer (e.g. RenderMan): export RIB files from Maya, then render with bash commands and Python
Bash Commands
- Check out cheat-sheet for commonly used commands:
Bash Scripts
Check out bash folder for bash scripts (.sh files for Linux, .bat files for Windows):
- ccrop.sh: crop with target center, and target width and height
- convert.bat: batch convert EXR files to PNG files
- deleteLines.sh: delete lines in (RIB) files with line numbers and from the file end
- makeVideo.sh: make video for a given folder with given name
- replace.sh: replace strings for all (RIB) files in a folder
- vcrop.sh: crop left and right of an image with target width
Python Scripts
- render.py: batch render RIB files
- convert.py: convert particles positions in TXT to OBJ/RIB
Content Creation Softwares
Maya
- Industry standard software
- Free education version available, renews every year
- Download education version at https://www.autodesk.com/education/edu-software/overview
- Recommended tutorial:
- Intro to Maya Series by Maya Learning Channel @YouTube
- Maya 2019 Fundamentals @PluralSight, preview ___
- To install Maya on Ubuntu, check this install guide that worked for me
- Check out my cheat-sheet for Python for Maya :
- Check out my scripts to use MEL or Python in Maya:
- animation.mel: animate a sequence of objects by hiding and displaying them in order
- animation.py: animate one (selected) object according to a TXT file
Blender
- Free, open-source, handy, and beginner-friendy
- Download at https://www.blender.org/
- Recommended tutorial:
- Blender Guru @YouTube, and his newest Blender 3.0 beginner donut tutorial
- Grant Abbitt @YouTube, and his complete beginners guide ___
- Check out my scripts to use Python in Blender:
- import-batch.py: import a sequence of obj files
- animate.py: animate a sequence of objects by hiding and displaying them in order
- shader.py: apply shader to a sequence of objects
RenderMan
- Free non-commercial license available, renew required every 3 months
- Download at https://renderman.pixar.com/store
- Recommended tutorial:
- RenderMan Docs: official RenderMan Docs, installation guides, plugins guides
- Learn RenderMan: official RenderMan learning resources
- Small Robot Studio @YouTube: learn specific RenderMan shading features ___
- To install RenderMan and RenderMan for Maya on Ubuntu, check this install guide that worked for me
Houdini
- Procedural generation software, commonly used for visual effects
- Many versions, including free and indie version, avaialble at https://www.sidefx.com/buy/
- Recommended tutorial:
- Learning Houdini: official SideFX get started tutorial
- Check out options to use houdini for meshing
Q&A
- Q: What OS should I use?
A: You can use the OS that you’re most comfortable with to get started. Most softwares support Windows, Mac OS, and Linux. Since rendering is a time-consuming and expensive work, when you need to render animation, you may want to utilize other machine(s) with a different OS. We will add more about transferring contents between different OS.
Resources
- Bash scripting cheatsheet: devhints.io/bash
- Python for Maya commands: Docs (2017 version)
- Udemy: 3D and Animation courses, high-quality with regular discounts
Publications
Publications using the rendering process:
(latest publication first)
-
A Unified Second-Order Accurate in Time MPM Formulation for Simulating Viscoelastic Liquids with Phase Change
Haozhe Su, Tao Xue, Chengguizi Han, Chenfanfu Jiang and Mridul Aanjaneya (*Joint first authors)
ACM Transactions on Graphics, (SIGGRAPH proceedings), 40, 4, 119:1-18, (2021)
Paper page: Paper | BibTeX | Video | Code
Featured in SIGGRAPH Technical Papers Video Trailer, starting at 2:44 -
A Novel Discretization and Numerical Solver for Non-Fourier Diffusion
Tao Xue, Haozhe Su, Chengguizi Han, Chenfanfu Jiang and Mridul Aanjaneya (*Joint first authors)
ACM Transactions on Graphics, (SIGGRAPH Asia proceedings), 39, 6, 178:1-14, (2020)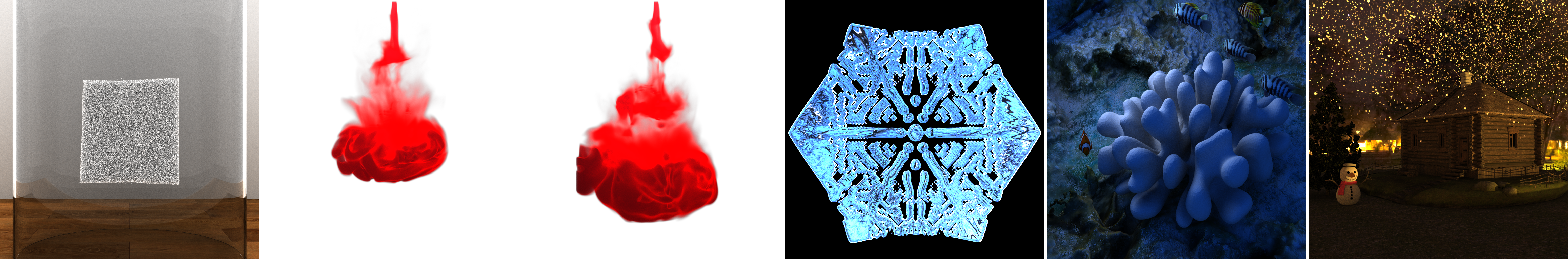 Paper page: Paper | BibTeX | Video | Code
Paper page: Paper | BibTeX | Video | Code -
A First Principles Approach for Data-Efficient System Identification of Spring-Rod Systems via Differentiable Physics Engines
Kun Wang, Mridul Aanjaneya and Kostas Bekris
Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, (2nd Annual Conference on Learning for Dynamics and Control), 120:1-15, (2020)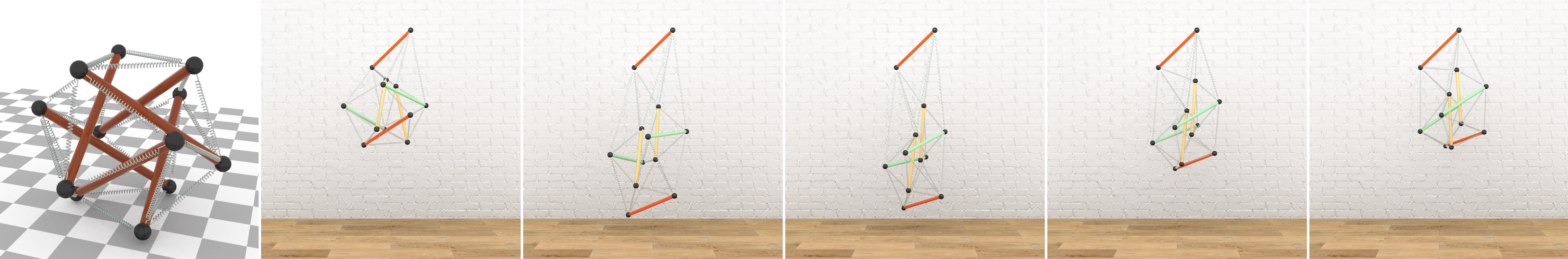
Paper page: Paper | BibTeX | Video -
An Efficient Geometric Multigrid Solver for Viscous Liquids
Mridul Aanjaneya, Chengguizi Han, Ryan Goldade and Christopher Batty (Lead and supervising author)
Proceedings of the ACM in Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, (SCA proceedings), 2, 2, 14:1-21, (2019)
Paper page: Paper | BibTeX | Video